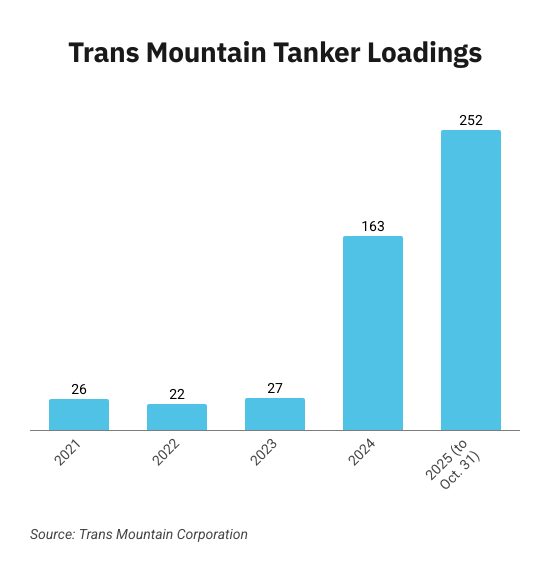
The Trans Mountain system continues its decades-long record of zero marine spills even as oil tanker traffic has surged more than 800 per cent since the pipeline’s expansion in May 2024.
The number of tankers calling at Trans Mountain’s Westridge Marine Terminal in the Port of Vancouver in one month now rivals the number that used to go through in one year.
A global trend toward safer tanker operations
The Westridge Marine Terminal loaded its first oil tanker shipment on January 1, 1956.
Nearly 70 years and a major expansion later, Trans Mountain’s ongoing safe marine operations are part of a worldwide trend.
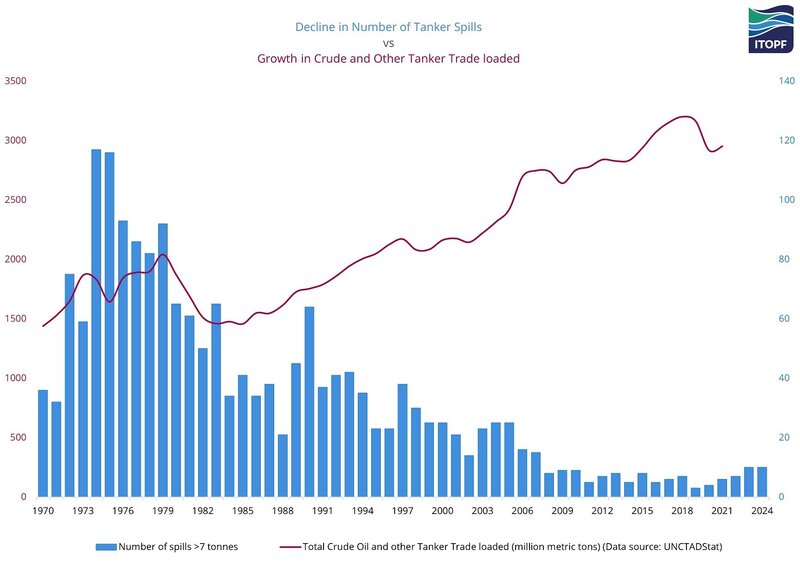
Global oil tanker traffic is up, yet marine spills are down, according to the International Tanker Owners Pollution Federation, a London, UK-based nonprofit that provides data and response support.
Transport Canada reports a 95 per cent drop in ship-source oil spills and spill volumes since the 1970s, driven by stronger ship design, improved response and better regulations.
“Tankers are now designed much more safely. They are double-hulled and compartmentalized to mitigate spills,” said Mike Lowry, spokesperson for the Western Canada Marine Response Corporation (WCMRC).
WCMRC: Ready to protect the West Coast
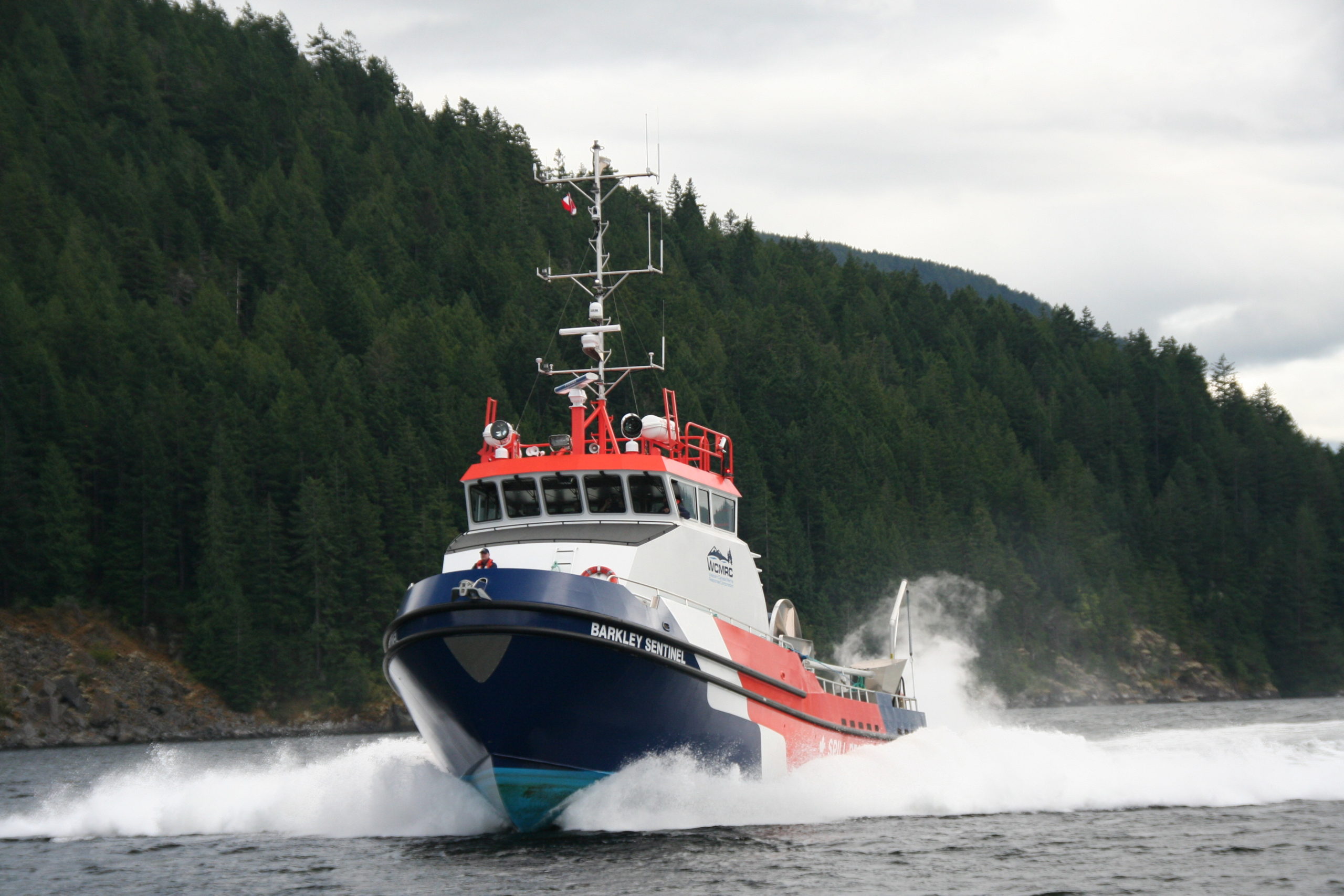

One of WCMRC’s new response vessels arrives in Barkley Sound. Photo courtesy Western Canada Marine Response Corporation
From eight marine bases including Vancouver and Prince Rupert, WCMRC stands at the ready to protect all 27,000 kilometres of Canada’s western coastline.
Lowry sees the corporation as similar to firefighters — training to respond to an event they hope they never have to see.
In September, it conducted a large-scale training exercise for a worst-case spill scenario. This included the KJ Gardner — Canada’s largest spill response vessel and a part of WCMRC’s fleet since 2024.
“It’s part of the work we do to make sure everybody is trained and prepared to use our assets just in case,” Lowry said.
Expanding capacity for Trans Mountain
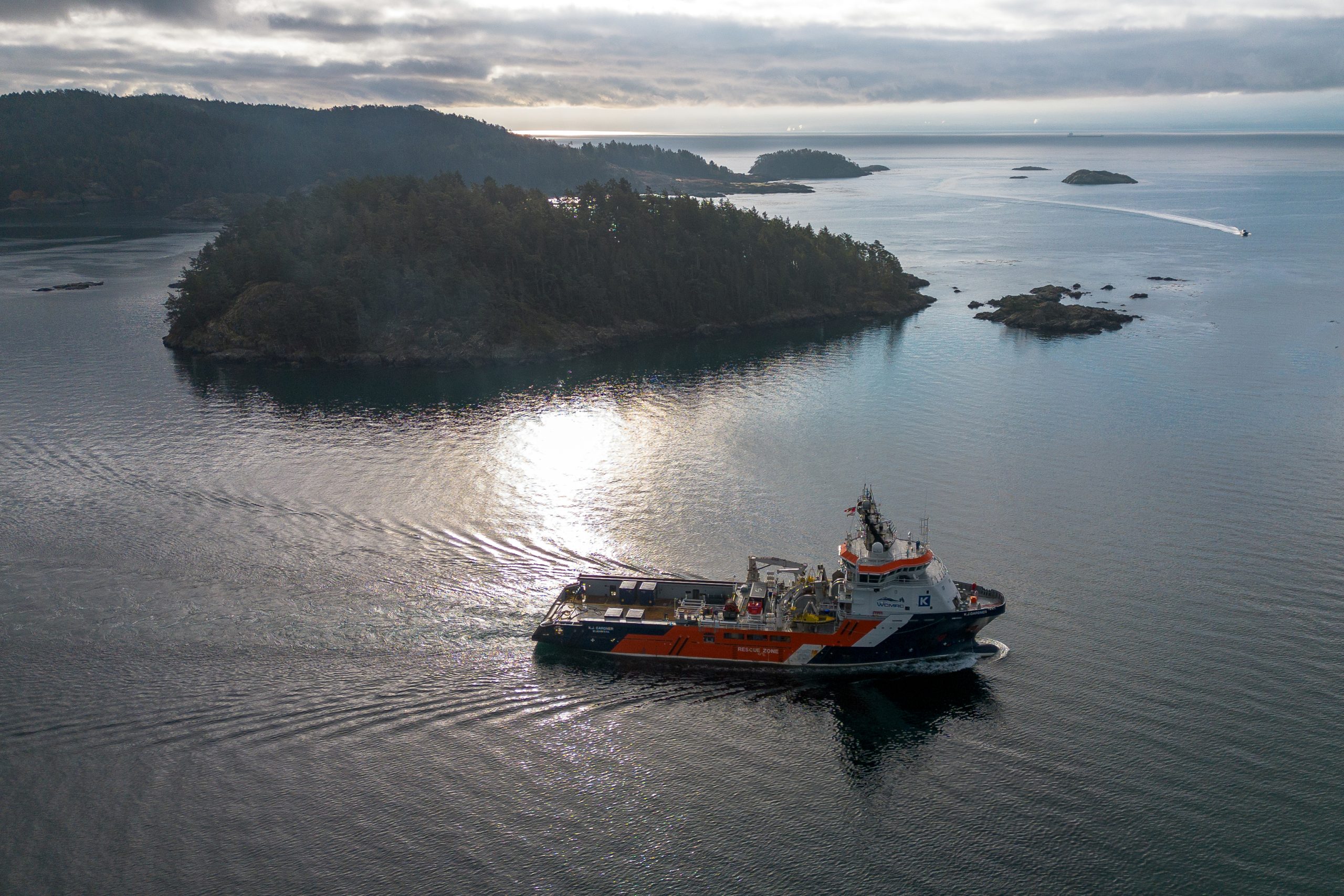

The K.J. Gardner is the largest-ever spill response vessel in Canada. Photo courtesy Western Canada Marine Response Corporation
WCMRC’s fleet and capabilities were doubled with a $170-million expansion to support the Trans Mountain project.
Between 2012 and 2024, the company grew from 13 people and $12 million in assets to more than 200 people and $213 million in assets.
“About 80 per cent of our employees are mariners who work as deckhands, captains and marine engineers on our vessels,” Lowry said.
“Most of the incidents we respond to are small marine diesel spills — the last one was a fuel leak from a forest logging vessel near Nanaimo — so we have deployed our fleet in other ways.”
Tanker safety starts with strong rules and local expertise
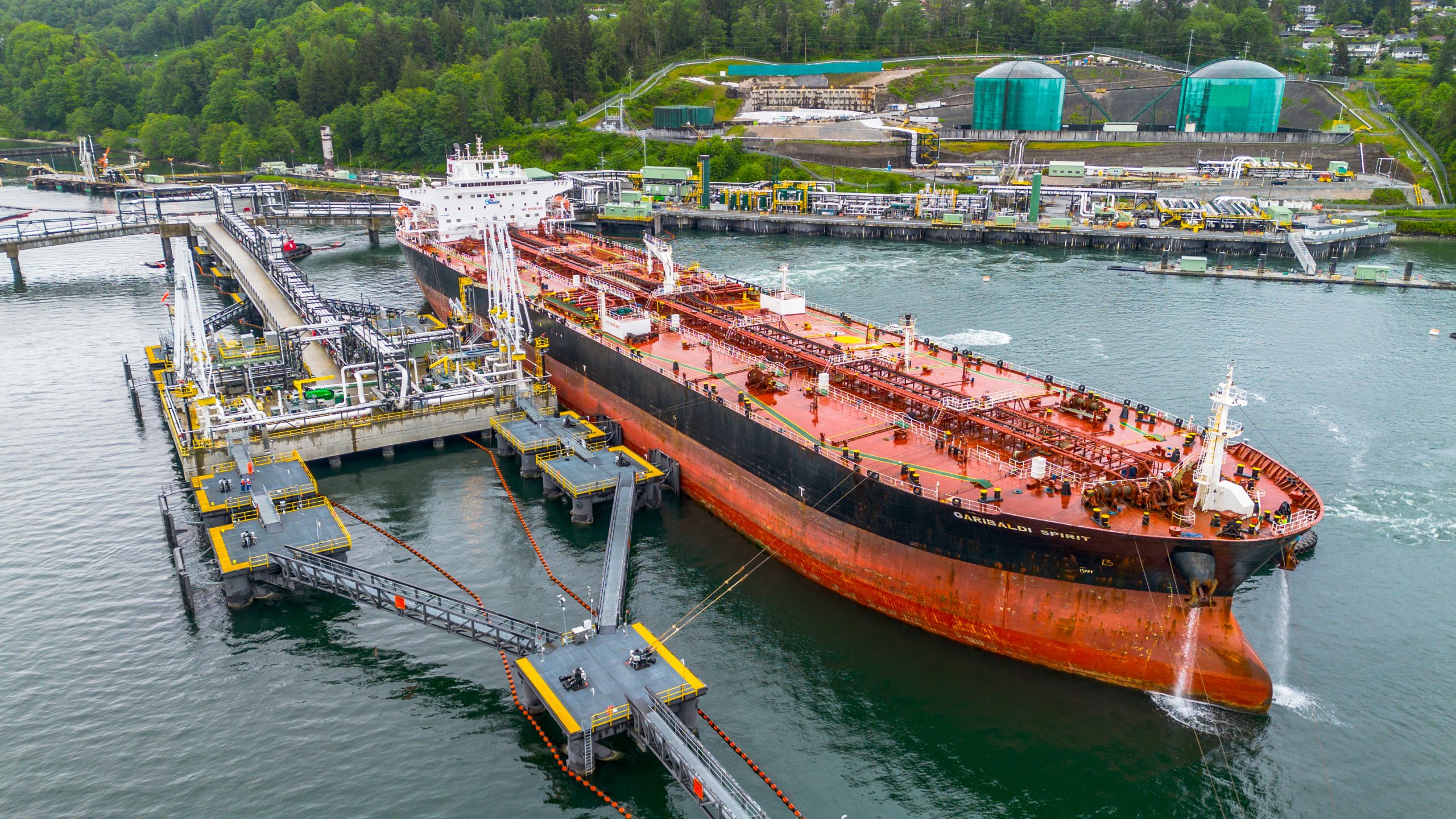

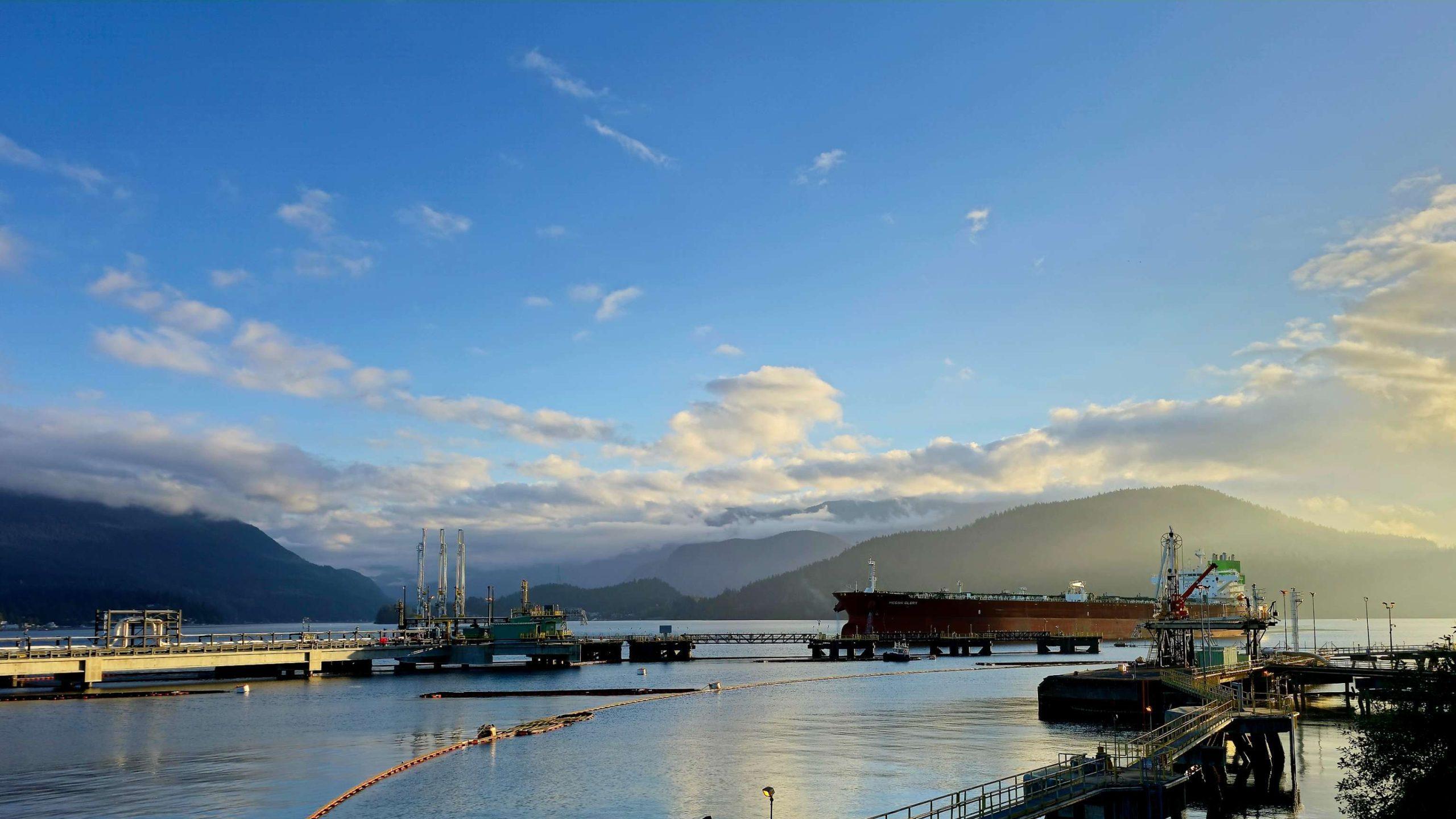
Tanker loading at the Westridge Marine Terminal in the Port of Vancouver. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
Speaking on the ARC Energy Ideas podcast, Trans Mountain CEO Mark Maki said tanker safety starts with strong regulations, including the use of local pilots to guide vessels into the harbour.
“On the Mississippi River, you have Mississippi River pilots because they know how the river behaves. Same thing would apply here in Vancouver Harbour. Tides are strong, so people who are familiar with the harbor and have years and decades of experience are making sure the ships go in and out safely,” Maki said.
“A high standard is applied to any ship that calls, and our facility has to meet very strict requirements. And we have rejected ships, just said, ‘Nope, that one doesn’t fit the bill.’ A ship calling on our facilities is very, very carefully looked at.”
Working with communities to protect sensitive areas
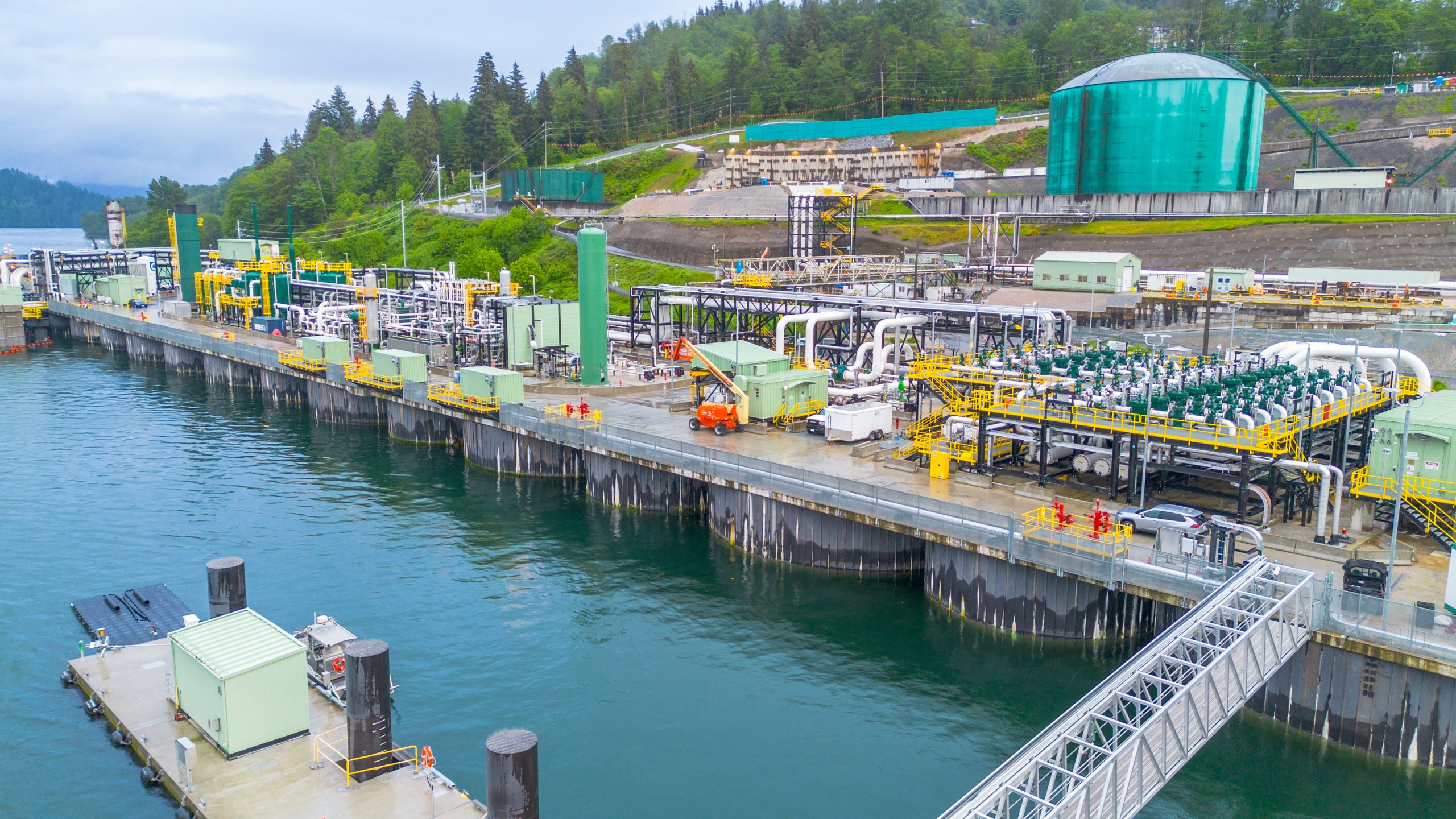

Trans Mountain’s Westridge Marine Terminal at Burnaby, B.C. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
Beyond escorting ships and preparing for spills, WCMRC partners with coastal communities to map sensitive areas that need rapid protection including salmon streams, clam beds and culturally important sites like burial grounds.
“We want to empower communities and nations to be more prepared and involved,” Lowry said.
“They can help us identify and protect the areas that they value or view as sensitive by working with our mapping people to identify those areas in advance. If we know where those are ahead of time, we can develop a protection strategy for them.”
The unaltered reproduction of this content is free of charge with attribution to the Canadian Energy Centre.